Discover how healthcare systems are moving beyond AI pilots to implement continuous-learning models that deliver measurable ROI. Learn proven strategies for scaling AI through process reengineering, federated data networks, and workflow integration in 2026.
The healthcare industry stands at a pivotal inflection point. After years of experimental AI pilots that promised transformation but often delivered limited results, forward-thinking health systems are now embracing a fundamentally different approach: collaborative, continuous-learning AI models that integrate seamlessly into clinical workflows and deliver measurable return on investment.
As of February 2026, the healthcare AI market has expanded to over $45 billion, with nearly 90% of hospitals adopting AI-driven diagnostics and remote monitoring technologies. Yet the gap between AI adoption and actual clinical impact remains substantial. The organizations achieving transformative results share a common strategy: they treat AI not as standalone technology but as an integrated capability requiring process redesign, federated data networks, and continuous validation.

Why Traditional AI Pilots Fail in Healthcare The healthcare industry has invested billions in AI pilots over the past five years, yet research from Boston Consulting Group reveals that successful organizations concentrate on a small number of opportunities with transformative potential rather than implementing dozens of AI pilots. The reason is straightforward: technology grafted onto outdated workflows rarely produces value.
Consider predictive surgical complexity algorithms. These tools can estimate operative difficulty weeks in advance with remarkable accuracy. However, without redesigning scheduling practices, operating room allocation, and staffing models to act on those predictions, the technology simply adds administrative burden. Healthcare leaders are learning that AI's value emerges not from the sophistication of algorithms but from the systems built around them.
The Continuous-Learning Model: From Pilots to Routine Care Leading healthcare platforms are now deploying hundreds of continuously operating algorithms that identify conditions before symptoms manifest. According to industry analysts, AI will accelerate from being used primarily as a cost-cutting tool to increasingly becoming a strategic driver of innovation across the healthcare ecosystem.
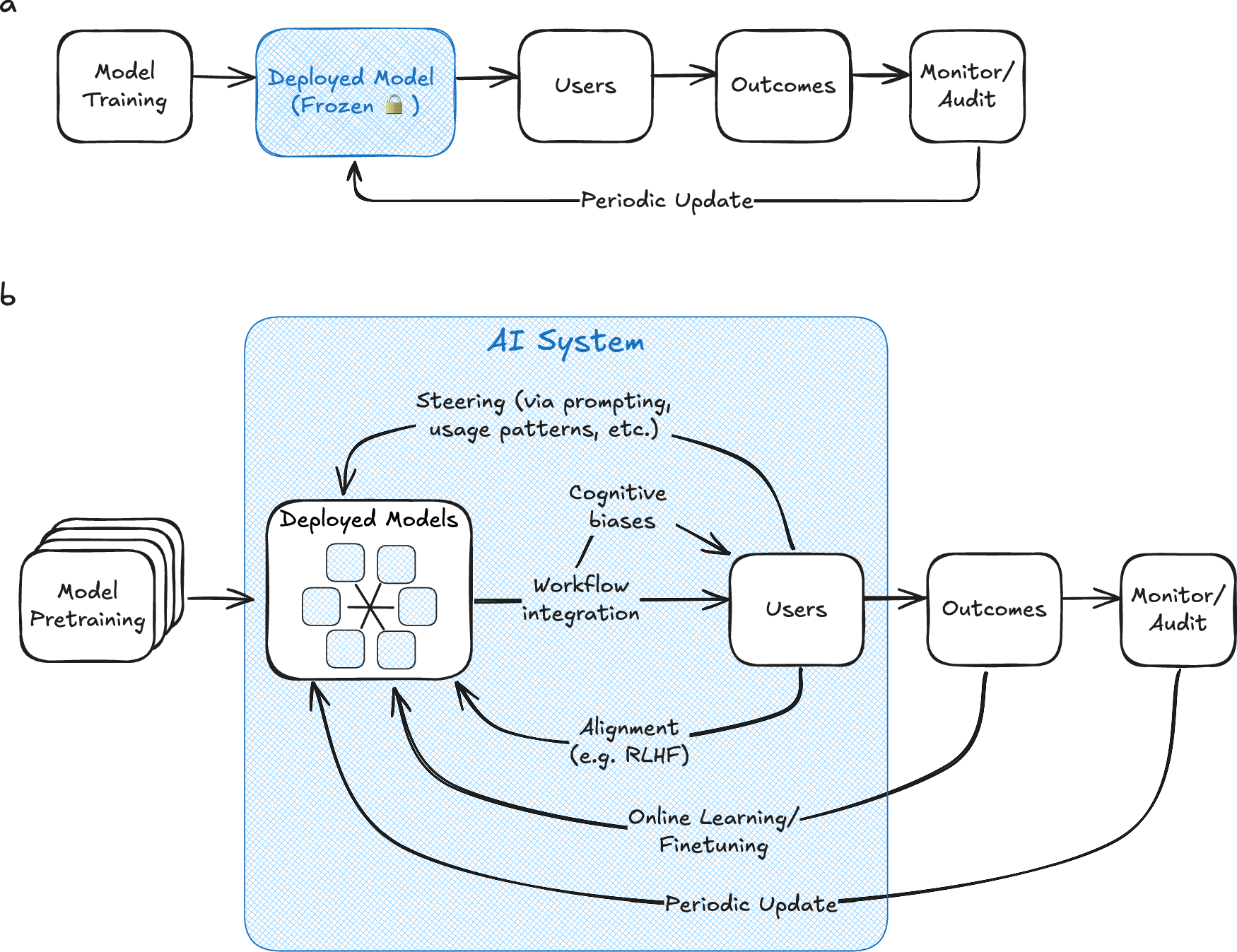
The Binary Test for AI Deployment Healthcare executives at the forefront of AI implementation apply a simple criterion: does the AI deployment either fundamentally change a care process or become a routine instrument of care, comparable to an MRI or stethoscope? This binary distinction separates projects delivering lasting impact from those that stall after pilot phase.
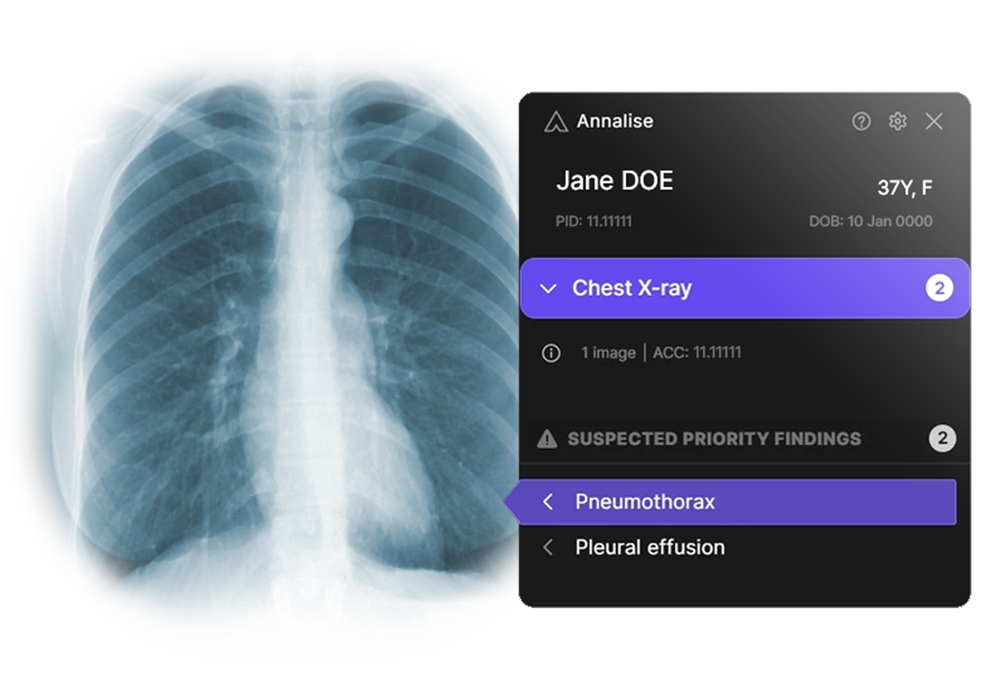
Examples of transformative AI deployment include: • Predictive models for heart failure exacerbations based on weight gain patterns and activity reduction, integrated into care coordinator workflows with automated alert protocols • Ambient documentation systems that reduce physician administrative burden by 15-20 hours per week, with CMS acceptance of AI-generated progress notes for billing purposes expected by mid-2026 • Radiology prioritization algorithms that triage critical findings while augmenting rather than replacing radiologist expertise • Virtual nursing platforms enhanced with anomaly detection providing 24/7 patient monitoring and reducing readmission rates

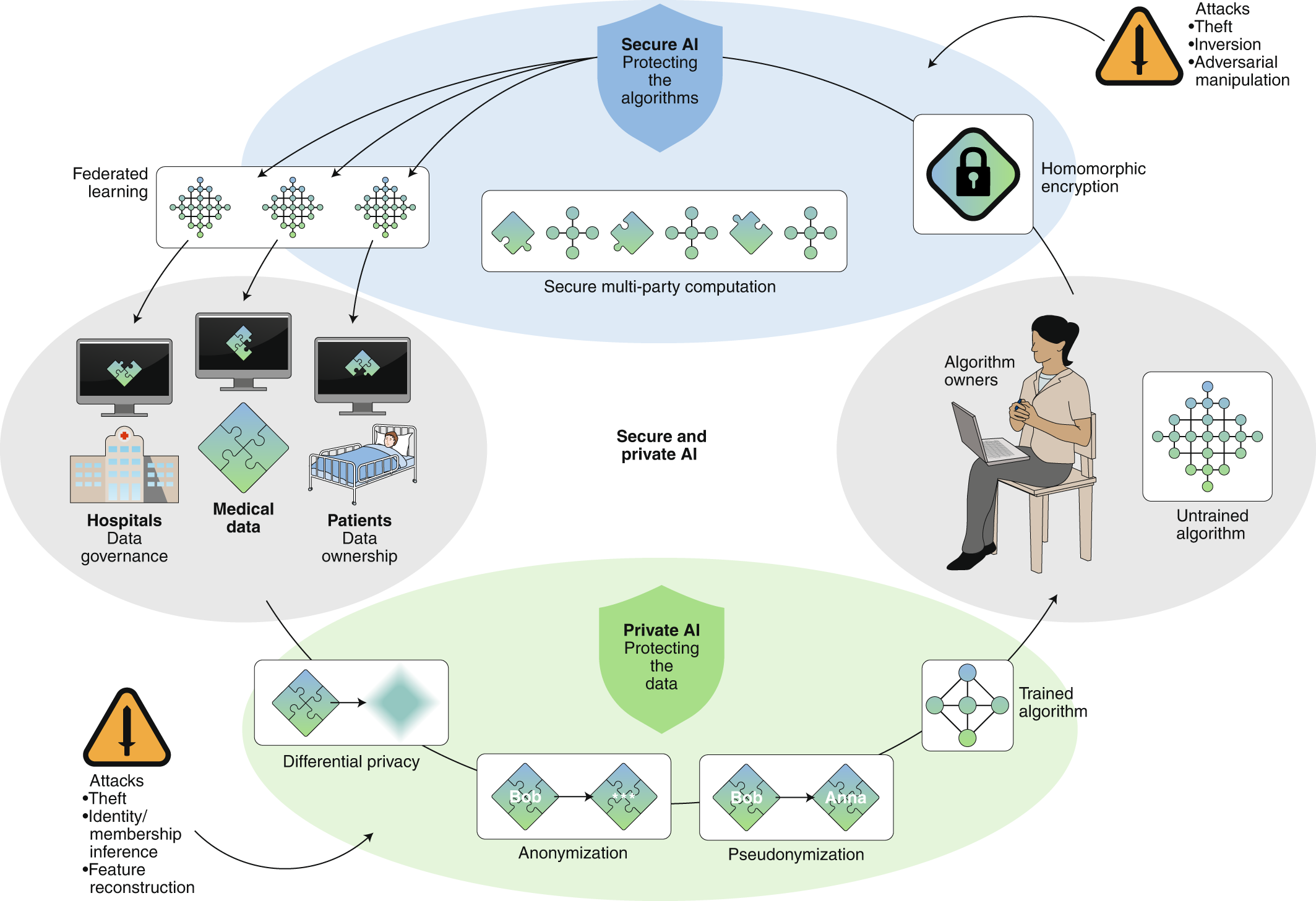
Building Trust Through Federated Data Networks One of healthcare AI's most significant challenges involves the risk of deploying models trained on narrow or geographically limited datasets. When algorithms perform well in academic medical centers but fail in community hospitals, the consequences extend beyond poor predictions to eroded clinician trust.
The Federated Learning Advantage Progressive healthcare platforms advocate federated data networks that enable AI models to learn from diverse populations without centralizing sensitive patient records. This approach addresses multiple concerns simultaneously: • Privacy Protection: Patient data never leaves the originating institution, with only model parameters and aggregate insights shared across the network • Population Diversity: Models trained on federated networks demonstrate improved performance across demographic groups, reducing algorithmic bias • Regulatory Compliance: Federated architecture aligns with HIPAA requirements and emerging state-level AI regulations while facilitating data sharing agreements • Continuous Improvement: As participating institutions encounter edge cases and rare conditions, the collective network benefits without requiring data centralization
Independent Validation: The Foundation of Clinical Credibility Healthcare AI distinguished itself from other sectors through its rigorous validation requirements. While consumer technology companies can iterate rapidly with minimal oversight, clinical AI demands external, population-diverse testing before broader deployment.
Research from Wolters Kluwer Health emphasizes that clinical-grade generative AI can be a trusted copilot when embedded in daily workflows, rigorously validated, protected by guardrails, and infused with expert-in-the-loop oversight. This principle applies across AI applications, from diagnostic support to treatment recommendations.
What Independent Validation Reveals Independent validation consistently uncovers performance gaps invisible during internal testing. Common findings include sensitivity variations across age groups, reduced accuracy in patients with multiple comorbidities, and challenges with rare presentations that dominate in academic centers but occur infrequently in community practice.
Organizations implementing validation frameworks report that approximately 30% of AI tools demonstrating excellent performance in development environments require substantial modification before clinical deployment. This validation phase, while time-consuming, prevents the costly mistakes that erode physician trust and institutional credibility.
Pre-Integration: Reducing Deployment Friction Healthcare IT leaders identify integration complexity as a primary barrier to AI adoption. Legacy electronic health record systems, fragmented data sources, and competing vendor priorities create substantial deployment friction. Pre-integrated solutions that fit seamlessly into existing workflows address this challenge directly.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is advancing this agenda through its 2026 Health Tech Ecosystem initiative, which requires participating applications to use modern identity solutions, integrate conversational AI chatbots, and adhere to Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards. Over 600 healthcare organizations have joined this voluntary pledge since its July 2025 launch.
Measuring What Matters: Defining AI Success Metrics Healthcare organizations pursuing AI implementation without clear success metrics frequently struggle to demonstrate value. Leading health systems now establish precise, outcome-focused measurements aligned with institutional priorities before deploying AI tools.
Four Categories of AI Impact Measurement
- Clinical Outcomes Mortality rates, complication frequencies, early detection of deterioration, medication error reduction, and adherence to evidence-based protocols. For sepsis prediction algorithms, success metrics include time-to-antibiotic administration, ICU admission rates, and 30-day mortality among flagged patients.
- Operational Efficiency Operating room utilization, emergency department throughput, length of stay optimization, and staffing productivity. McKinsey projects AI could increase healthcare productivity by 1.8-3.2% annually, equivalent to $150-260 billion per year, primarily through workflow optimization and administrative automation.
- Financial Performance Revenue cycle improvement, prior authorization processing time, denial rate reduction, and cost per case. A 1,000-physician health system processing 50,000 prior authorizations annually can achieve approximately $1.1 million in annual savings through AI automation while reducing authorization processing from days to hours.
- Patient Access and Experience Wait times for appointments, time to specialist consultation, patient satisfaction scores, and care continuity metrics. AI-powered scheduling and triage systems can increase clinical capacity by 30-40% without adding providers.
Addressing Privacy and Building Clinician Trust Patient privacy protection remains fundamental as healthcare systems pursue digital transformation. The emergence of shadow AI—unauthorized use of consumer AI tools by clinical staff seeking efficiency gains amid persistent burnout—has forced healthcare leaders to implement more formalized organization-wide AI governance frameworks.
2026 Governance Priorities Progressive organizations are standardizing baseline AI literacy through formal training programs covering privacy protocols, transparency requirements, monitoring procedures, and human-in-the-loop expectations. These programs extend beyond clinical staff to encompass administrators, technical personnel, and leadership teams.
Key governance components include: • Comprehensive audit trails documenting AI usage, decisions influenced by algorithmic recommendations, and override patterns indicating potential bias or performance issues • Regular bias audits examining AI performance across demographic subgroups, with mandatory retraining when disparities emerge • Transparent disclosure policies informing patients when AI contributes to diagnosis, treatment recommendations, or care coordination decisions • Clinical validation committees with representation from multiple specialties, nursing leadership, quality improvement, and patient advocacy
Overcoming Legacy IT and Clinician Adoption Barriers Technical barriers represent only part of the AI adoption challenge. Research examining physician workflow found that documentation and administrative work consume nearly twice as much time as direct patient care. This reality creates both opportunity and risk for AI deployment.
The Clinician Buy-In Imperative Healthcare leaders report that AI tools demonstrating clear time savings and workflow improvement achieve rapid adoption, while those adding complexity—even with superior algorithms—face resistance. The most successful implementations involve clinicians throughout the development and deployment process, from initial workflow analysis through pilot testing and iterative refinement.
A survey of healthcare professionals found that 86% were comfortable either fully delegating or having AI assist with identifying easy-to-miss details across patient records, provided the technology brings clarity rather than complexity. This comfort level drops precipitously when AI requires additional documentation, manual data entry, or disrupts established clinical patterns.
Global Deployment: Adapting AI Across Healthcare Systems Healthcare AI solutions developed and validated in high-resource academic medical centers frequently underperform when exported to different healthcare environments. Population demographics, disease prevalence, clinical practice patterns, and available diagnostic resources vary substantially across regions, requiring adaptive deployment strategies.
Leading AI platforms prioritize pre-validation across multiple healthcare environments, establishing baseline performance expectations before broader rollout. This approach identifies necessary adaptations—from algorithm retraining on local populations to interface modifications accommodating different clinical workflows—before they impede adoption.
The 2026 Healthcare AI Landscape: Consolidation and Maturation Industry analysts project significant consolidation within the healthcare AI vendor landscape during 2026. Multiple point solution providers addressing narrow use cases—ambient documentation, radiology prioritization, sepsis prediction—are expected to merge, offering more comprehensive platforms that reduce vendor management complexity for healthcare organizations.
This consolidation reflects healthcare systems' evolving purchasing preferences. While early adopters willingly experimented with multiple AI tools testing different use cases, mature organizations increasingly seek integrated platforms reducing interoperability challenges, simplifying governance, and delivering economies of scale.
Funding Patterns and Market Dynamics Healthcare AI companies captured approximately 40% of overall digital health funding in 2025, with that proportion expected to increase in 2026. However, funding concentration is shifting toward fewer, more mature platforms demonstrating scaled deployment, user trust, and successful navigation of implementation challenges. Healthcare AI startups raised over $7 billion in venture capital during 2024, with the largest investments targeting ambient documentation, clinical decision support, and revenue cycle optimization.
Regulatory Evolution: Balancing Innovation and Safety The regulatory landscape for healthcare AI remains fragmented and evolving. In December 2024, President Donald Trump signed an executive order potentially preempting some state AI regulations and calling for a national framework. The Assistant Secretary for Technology Policy subsequently proposed rules removing AI model card certification requirements, signaling federal preference for reduced oversight.
However, states continue proposing AI legislation addressing algorithm transparency, bias testing, and liability frameworks. Healthcare organizations must navigate this complex regulatory environment while implementing AI tools, creating tension between innovation velocity and compliance requirements.
Progressive health systems are responding by implementing governance standards exceeding current regulatory requirements, recognizing that today's voluntary best practices frequently become tomorrow's mandatory compliance obligations. This proactive approach reduces future adaptation costs while demonstrating organizational commitment to responsible AI deployment.
Practical Implementation: From Strategy to Execution Organizations achieving transformative AI outcomes follow disciplined implementation frameworks distinguishing them from struggling peers. These frameworks prioritize strategic alignment over technological sophistication.
The Seven-Phase Implementation Model Phase 1: Strategic Alignment Identify AI opportunities directly addressing institutional priorities—reducing length of stay, improving margin on surgical cases, enhancing primary care access, or decreasing preventable readmissions. Avoid technology-driven projects lacking clear connection to strategic objectives.
Phase 2: Workflow Analysis Map current state workflows with frontline staff participation, identifying pain points, redundancies, and inefficiencies that AI might address. Document time allocations, handoff procedures, information requirements, and decision points requiring clinical judgment.
Phase 3: Process Redesign Design future state workflows incorporating AI capabilities, ensuring technology changes how work is performed rather than simply automating existing inefficiencies. This phase determines whether AI deployment will deliver transformative value or incremental improvement.
Phase 4: Technology Selection and Validation Evaluate AI vendors using standardized criteria emphasizing integration capabilities, validation evidence, implementation support, and ongoing performance monitoring. Conduct pilot testing in controlled environments before broader deployment.
Phase 5: Change Management and Training Develop comprehensive training programs addressing both technical proficiency and conceptual understanding of AI capabilities and limitations. Establish super-user networks providing peer support during initial deployment phases.
Phase 6: Measured Deployment Implement AI tools through staged rollout enabling rapid identification and correction of implementation challenges. Monitor pre-defined success metrics continuously, adjusting workflows and training based on real-world performance.
Phase 7: Continuous Optimization Establish ongoing governance processes reviewing AI performance, addressing emerging challenges, and identifying optimization opportunities. Successful organizations treat AI deployment as iterative improvement rather than one-time implementation.
The Future Vision: AI-Enhanced Healthcare by 2030 While 2026 represents healthcare AI's transition from experimentation to operational integration, the trajectory extends substantially further. Industry leaders envision healthcare systems where AI operates as seamlessly as current diagnostic technologies—present in workflows but largely invisible to patients.
This future encompasses several transformative capabilities now emerging from research and early deployment: • Proactive Care Models: Healthcare shifting from reactive treatment to predictive prevention, with AI identifying risk trajectories years before symptom onset • Precision Medicine at Scale: Genomic analysis integrated with clinical data and environmental factors enabling truly personalized treatment selection within hours rather than weeks • Automated Administrative Burden: Clinical documentation, prior authorization, medication reconciliation, and discharge planning handled by AI with physician oversight rather than physician execution • Continuous Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and home sensors providing real-time health data enabling early intervention before conditions require emergency care or hospitalization • Augmented Surgical Planning: AI analyzing patient anatomy, surgical videos, and outcomes data to provide technique recommendations and complication risk assessments
Conclusion: Technology as Enabler, Not Solution The healthcare AI revolution of 2026 demonstrates a fundamental truth: sophisticated algorithms alone do not transform clinical care. Organizations achieving measurable impact from AI deployment share common characteristics—disciplined process reengineering, comprehensive validation, transparent governance, and relentless focus on workflow integration.
As one chief operating officer emphasized, moving from symptom-based care to early intervention changes outcomes and creates real value. This shift requires more than predictive algorithms; it demands healthcare systems willing to fundamentally reimagine clinical workflows, invest in continuous learning infrastructure, and maintain patient safety as the paramount objective.
The collaborative, continuous-learning model represents healthcare's path forward—not because it deploys the most sophisticated technology, but because it builds the systems, partnerships, and governance frameworks enabling AI to deliver transformative clinical impact. Organizations embracing this approach position themselves to lead healthcare's next evolution, while those pursuing technology-first strategies risk joining the growing list of failed AI pilots.
Success in healthcare AI ultimately depends less on algorithm sophistication and more on organizational commitment to the hard work of process transformation, continuous validation, and clinician engagement. The organizations that understand this distinction will define the future of healthcare delivery.
About the Author This comprehensive analysis synthesizes insights from leading healthcare AI platforms, academic research institutions, industry analysts, and frontline clinical implementation teams. The research incorporates findings from Boston Consulting Group, Wolters Kluwer Health, Harvard Med

Comments
Total: 0